Single Sideband Modulation
Conventional double sideband(DSB) modulation can be considered wasteful of power and bandwidth because they contain a carrier signal and two identical sidebands.
Conversely, single sideband(SSB) modulation, as the name implies, uses only one sideband to provide the final signal.
In other words, SSB provides a considerably more efficient form of communication when compared to DSB modulation.
It is far more efficient in terms of the radio spectrum used,
and also the power used to transmit the signal.
In view of its advantages,
SSB modulation has been widely used for many years, providing effective communications .
In terms of mathematics, let’s illustrate DSB as below :

A is carrier frequency, B is baseband(data) frequency.
Therefore, DSB modulation, as the name implies, provides two sidebands : (A+B) and (A-B).

As for SSB :

or

(A-B) is lower sideband(LSB), and (A+B) is upper sideband(USB).

And as illustrated below, there is exactly 90º phase offset between sine and cosine.

In terms of Unit Circle, the definition of Sine and Cosine are as below :

As illustrated above,
Cosine is in-phase, so we call it “I” signal.
And Sine is quadrature-phase, so we call it “Q”.

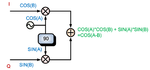
Thus, if we want to generate a (A-B) signal by means of SSB modulation,
the block diagram is as below :

Conventional double sideband(DSB) modulation can be considered wasteful of power and bandwidth because they contain a carrier signal and two identical sidebands.
Conversely, single sideband(SSB) modulation, as the name implies, uses only one sideband to provide the final signal.
In other words, SSB provides a considerably more efficient form of communication when compared to DSB modulation.
It is far more efficient in terms of the radio spectrum used,
and also the power used to transmit the signal.
In view of its advantages,
SSB modulation has been widely used for many years, providing effective communications .
In terms of mathematics, let’s illustrate DSB as below :
A is carrier frequency, B is baseband(data) frequency.
Therefore, DSB modulation, as the name implies, provides two sidebands : (A+B) and (A-B).
As for SSB :
or
(A-B) is lower sideband(LSB), and (A+B) is upper sideband(USB).
And as illustrated below, there is exactly 90º phase offset between sine and cosine.
In terms of Unit Circle, the definition of Sine and Cosine are as below :
As illustrated above,
Cosine is in-phase, so we call it “I” signal.
And Sine is quadrature-phase, so we call it “Q”.
Thus, if we want to generate a (A-B) signal by means of SSB modulation,
the block diagram is as below :